Fundamental Concepts
Crystalline (晶體) and amorphous (非晶體)
(classify according to the regularity with which atoms or ions are arranged with respect to one another)
Crystal – Three dimensional repeating pattern of atoms, ions, or molecules. (long range order exists

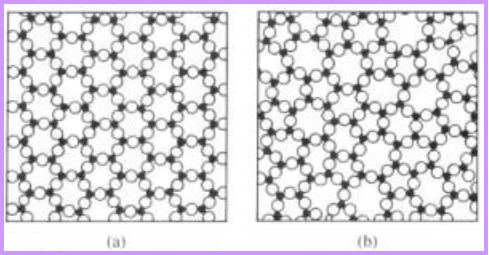
Structures of metals Structures of SiO2
Crystal structure - the manner in which atoms, ions, or molecuIes are spatially arranged.
Arrangements of atoms and ions play an importantrole in determining the properties of a material.
Lattices and Unit Cells 晶格和晶胞
For convenience, atomic arrangements in crystalline solids can be described by referring the atoms to the points of intersection of a network of lines in three dimensions. The surroundings of each point in the lattice are identical. This network is called lattice and the points of intersection are called lattice points.
Lattice means a three-dimensional array of points coinciding with atom positions(or sphere centers).
晶格:用假想的直線將原子中心連接起來所形成的三維空間格架。直線的交點(原子中心)稱結點。由結點形成的空間點的陣列稱空間點陣。
Unit cell- a small repeat entities (parallelepipeds or prisms) which was subdivided from the structure.Unit cell – have to represent the symmetry of the crystal structure, atom position in the crystal structure should be generated by translations of the unit cell integral distances along each of its edges.
晶胞:能代表晶體原子排列規律的最小幾何單元
- Relatively small unit - The highest level of geometrical symmetry
How to distinguish the size and shape of the different unit cells?
Lattice Constants/Parameters晶格常數: a, b, c – lattice vectors
Alpha (α), beta(β), gamma (γ) – interaxial angles

Lattice Constants
Typical Metallic Crystal Structures 典型的金屬晶體結構
Three densely packed crystal structures are
found for most elemental metals:
(1) body-centered cubic (BCC,體心立方)
(2) face-centered cubic (FCC,面心立方)
(3) hexagonal close-packed (HCP,密排六方)
1.Body-centered cubic (BCC) structure
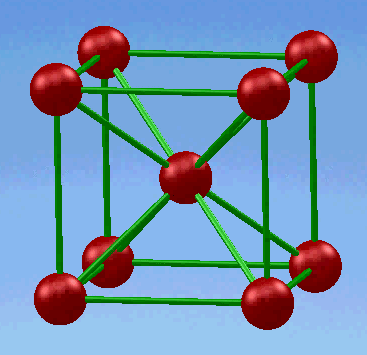
In this unit cell, eight atoms are located in all eight corners and a single atom is located at the cube center.
Two important characteristics of a crystal structure:
coordination number 配位數 - the number of the nearest neighbor atoms for an atom
atomic packing factor (APF) 致密度- the sum of the sphere volumes of all atoms within a unit cell divided by the unit cell volume

2. Face-centered cubic (FCC) structure
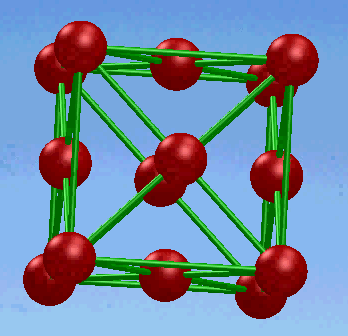
In this unit cell,there is one atom at each corner of the cube and one at the center of each cube face.
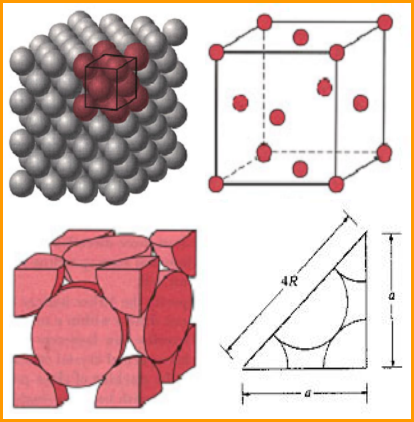
The coordination number of FCC structure is 12.The atomic packing factor for the FCC unit cell is 0.74,which is great than the 0.68 factor for the BCC structure.
Some of the familiar metals having FCC crystal structure are ?-Fe, Ni, Al, Ag, Au, and Pb(lead).
3. Hexagonal close-packed (HCP) structure
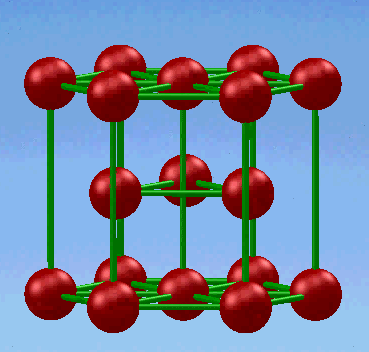
In this unit cell, the top and bottom faces consist of six atoms that form regular hexagons and surround a single atom in the center. Another plane that provides three additional atoms to the unit cell is situated between the top and bottom planes.
If a and c represent the short and long unit cell dimensions respectively.the c/a ratio for an ideal HCP structure consisting spheres packed as tightly together as possible is 1.633.The relationship between the lattice constant a and the atomic radius r is r=a/2 . The equivalent of six atoms is contained in the HCP structure,because each of the 12 top and bottom face corner atoms contribute one-sixth atom, each of the 2 center face atoms contribute one-half atom,and the three midplane interior atoms are wholly contained in the structure.
The coordination number and the atomic packing factor for the HCP crystal structure are 12 and 0.74,respectively.These data are the same as those for FCC, because in both structures the atoms are packed as tightly as possible.
The HCP metals include α-Ti, Mg, Zn, Be (beryllium) and Cd (cadmium)
Crystal Defects 晶體缺陷
Why study defects in solid?
Real crystals are never perfect and contain various types of defects.The properties of some materials are profoundly influenced by the presence of imperfections. Consequently, it is important to have a knowledge about the types of defects that exist and the roles they play in affecting the behavior of materials.
Crystal defects are generally classified according to their geometries and shapes.
點缺陷 Zero-dimensional or point defects;
線缺陷 One-dimensional or linear defects;
面缺陷 Two-dimensional or planar defects;
體缺陷 Three-dimensionaI bulks or volume defects.
(1 )Point Defects 點缺陷
A point defect typically involves one atom, or a pairof atoms. There are three types of point defects:Vacancy, interstitiaI defect, substitutionaI defect.
The simplest kind of point defect is a vacancy (空位).It is produced when an atom is absent from its normal site in the crystal structure.Since vacancies can be produced by atomic thermal vibration,all crystalline solids contain vacancies and it is not possible to create a material that is free of vacancies.
An interstitial defect (間隙原子) is formed when an extra atom inserts into the crystal structure at a normally unoccupied position.Interstitial atoms may either come from the crystal itself,i.e. ,self-interstitial,or come from outside as impurity or as a deliberate alloying addition.
A substitutional defect (置換原子) is introduced when one atom is replaced by a different type of atom and the substitutional atom occupies the normal lattice site.
Substitutional atoms may either be larger than the normal atoms in the crystal structure or smaller.
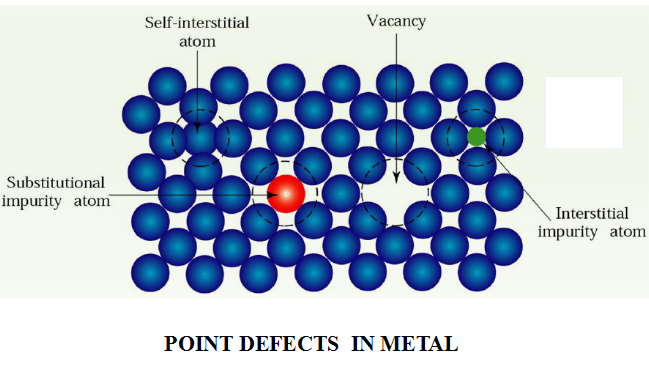
Because of the existence of point defects, the surrounding crystal region is distorted. Consequently,the properties of materials are affected.
For example with increasing density of point defects in metallic materials,the electrical resistivity,strength,and hardness improved,while the plastic property and toughness are decreased.
(2) Linear Defects 線缺陷
A dislocation 位錯 is a linear defect,around which some of the atoms are misaligned.
Dislocations are created during the solidification of crystalline solids. They are also formed by the permanent or plastic deformation of crystalline solids and by vacancy condensations and by atomic mismatch in solid solution.
Three types of dislocations can be identified:
the edge dislocation 刃型位錯,
the screw dislocation 螺型位錯,
and the mixed dislocation 混合位錯.

An edge dislocation is featured by an extra portion of a plane of atoms,or haIf plane.
The edge dislocation usually is represented by the symbol ⊥, which indicates the position of the dislocation line. This symbol also indicates a positive edge dislocation that the extra half plane is included in the upper portion 0f the crystal.
Screw dislocation 螺型位錯
The perfect crystal (a) is cut and sheared one atom spacing, (b) and (c). The line along which shearing occurs is a screw dislocation.

Mixed dislocations 混合位錯
Most dislocations found in crystalline materials are probably neither pure edge nor pure screw, but exhibit components of both types; these are termed mixed dislocations.
Conclusion: Dislocations
Dislocation - A line imperfection in a crystalline material.
Screw dislocation - A dislocation produced by skewing a crystal so that one atomic plane produces a spiral rampabout the dislocation.
Edge dislocation - A dislocation introduced into the crystal by adding an ‘extra half plane’ of atoms.
Mixed dislocation - A dislocation that contains partly edge components and partly screw components.
(3) Planar and Volume Defects面缺陷和體缺陷
Planar defects include:
external surface 外表面
grain boundaries 晶界
twin boundaries 孿晶界
stacking faults 層錯
phase boundaries 相界
Grain boundaries 晶界
Grain boundaries are imperfections in polycrystalline (多晶體) materials that separate grains with different crystallographic orientations (位向).
Volume defects are much larger than aforementioned imperfections.
These include pores孔洞, cracks裂紋, foreign inclusions夾雜物, and other phases相.They are formed during processing and fabrication steps.

| |

